Philippines outpaces global averages in GenAI adoption

Businesses are aggressively fostering a digitally confident workforce, with employers making artificial intelligence (AI) a core priority that demands employees acquire AI skills to remain competitive.
According to a study by the online learning platform Coursera, the Philippines has begun laying the groundwork for a digitally confident workforce, with the nation's rapid growth in enrollment in Generative AI (GenAI) courses significantly outpacing the global average.
“AI is a clear priority for employers, and learners are stepping up by acquiring GenAI skills and industry micro-credentials to stay ahead,” said Eklavya Bhave, Coursera Asia Pacific.
Coursera recently released its annual Global Skills Report, showing a 383 percent year-on-year increase in GenAI enrollments in the country.
Bhave noted that the Philippines' growth in enrollment far outpaced the Asia Pacific average of 132 percent and even the global average of 195 percent.
“From AI strategies to forward-thinking education policies, we’re seeing a strong national commitment to equipping Filipinos with the right mix of technical, business, and human skills,” Bhave said.
According to Coursera, this enrollment growth aligns with the Philippines’ efforts to upskill one million AI-skilled workers by 2028, as part of broader digitalization goals. To date, Bhave has stated that 86 percent of Filipino knowledge workers already utilize AI at work, surpassing the global average of 75 percent and the regional average of 83 percent.
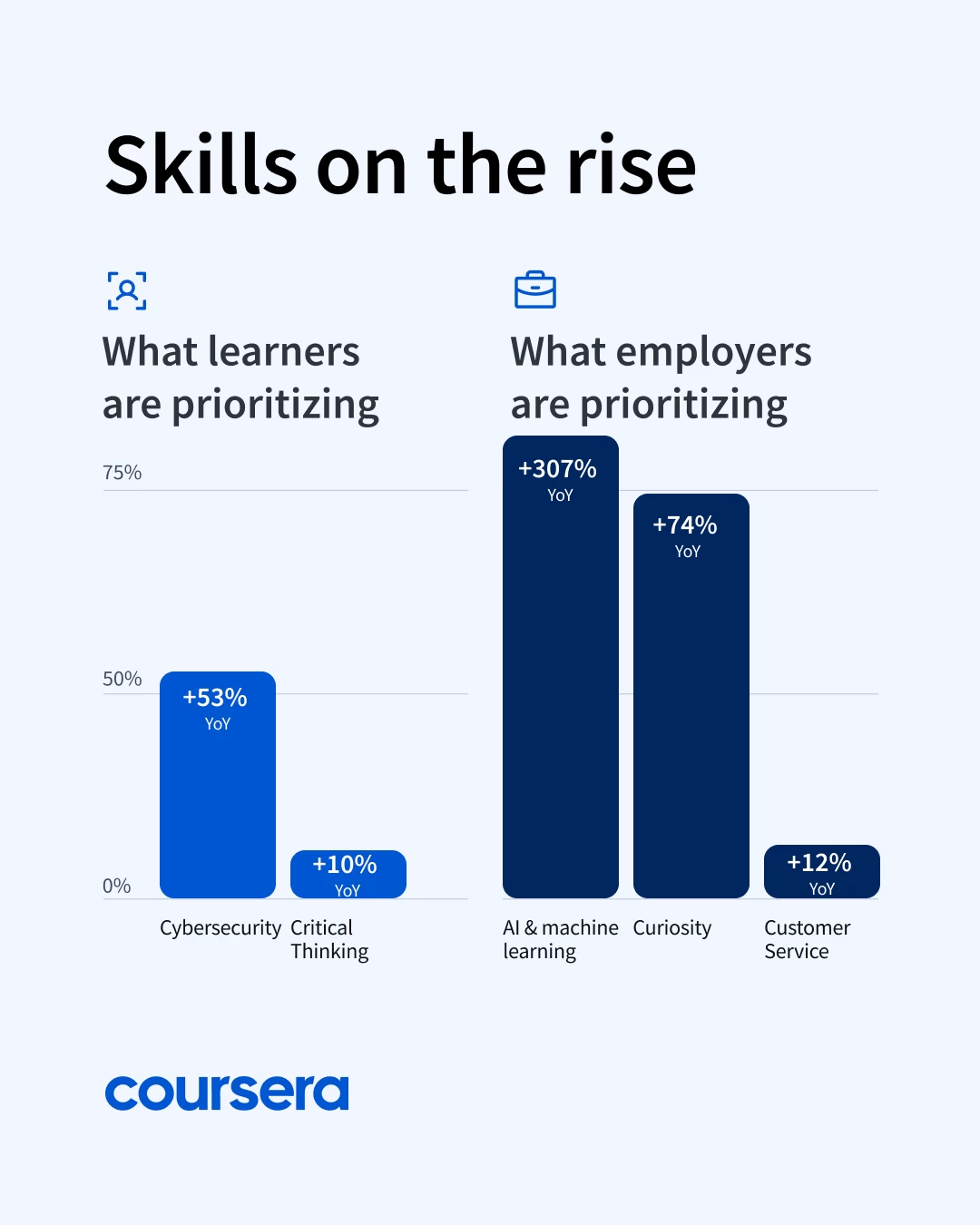
This trend is also echoed by learner behavior on Coursera, with a sharp rise in enrollments in courses that equip learners with skills employers are prioritizing: AI and ML (up 307 percent), Curiosity (up 74 percent), Customer Service (up 12 percent), and Critical Thinking (up 10 percent).
Addressing gaps and fostering future growth

However, while GenAI enrollments increased almost fivefold, participation gaps persist, with women comprising only 37 percent of these learners, despite representing 51 percent of Coursera’s overall learner base in the country.
Meanwhile, demand for job-ready credentials continues to rise in the Philippines, and enrollments in professional certificates grew by 23 percent from the previous year.
Filipino learners are also building applied tech and digital marketing skills as they prioritize practical skills in software development, IT infrastructure, and campaign management.
According to the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2025, 96 percent of Filipino businesses aim to upskill their workforce to work effectively alongside AI, surpassing the global average of 77 percent.
However, an International Monetary Fund report stated that 40 percent of jobs in the Philippines are significantly impacted by AI, with 14 percent of the workforce being directly at risk of displacement.
“Bridging the gap will require coordinated national efforts – including expanding public-private partnerships, integrating micro-credentials into higher education, and scaling online learning access,” Bhave said. “Increasing women’s participation in emerging technology fields will also be critical, not just to achieve gender equality, but to also unlock the full potential of the country’s digital economy,” he added.

In Coursera’s Global Skills Report, Filipino learners demonstrated 29 percent proficiency in business, 21 percent in technology, and 17 percent in data science. In Coursera’s AI Maturity Index, the country ranked 60th, indicating promising growth potential in AI research, innovation, and talent development.
Coursera has 2.7 million learners in the Philippines with a median age of 32, positioning itself as one of the region’s most digitally engaged populations.